Model Orientation
Rotation
-
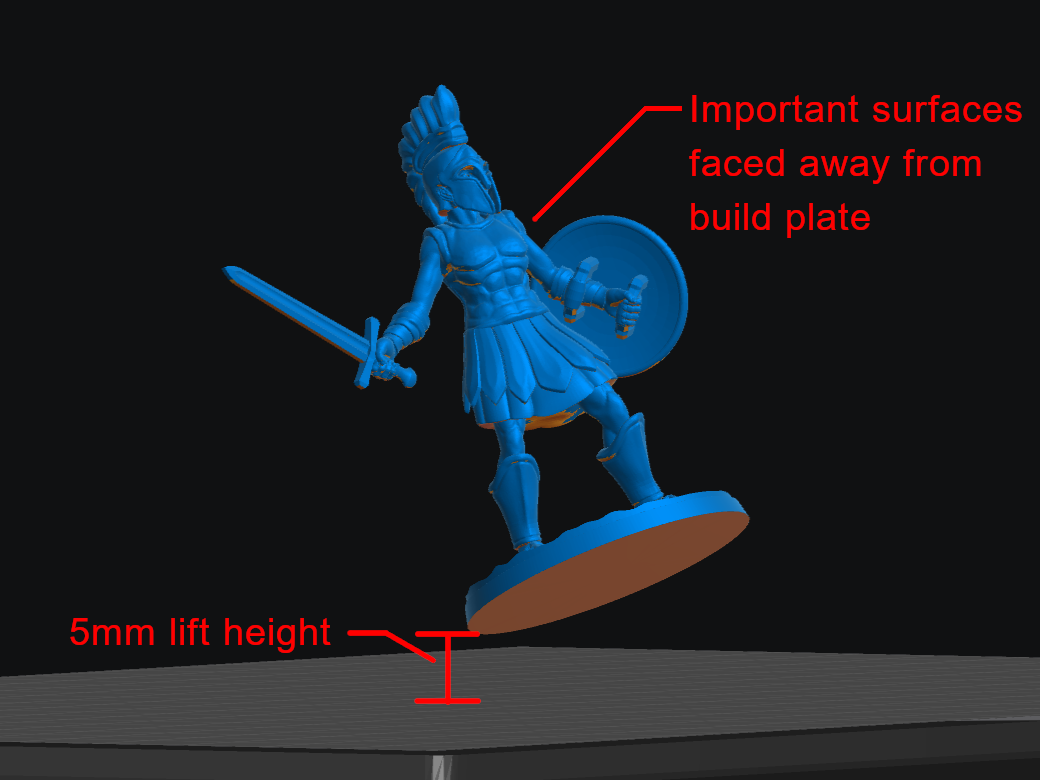
Identify the most important surfaces
For miniatures, this is typically the front and top. Rotate the model so these surfaces are faced up and away from the FEP and require no supports (or minimum supports).
-
Identify large cross sections & overhangs
Large cross section areas increase pull force and are prone to failure. If possible, rotate the model to reduce large cross section areas.
-
Identify tricky islands
Take note of any overhangs that supports will have trouble getting to. Monster teeth are a good example of this. It may be beneficial to rotate the model so that supports are either not required in these locations or have easier access to these locations.
-
Consider support height and print time
If your orientation makes the supported file excessively tall, you might want to consider alternate rotations to reduce the height. If reducing height is not possible, make sure tall supports have increased diameters and/or extra bracing supports.
Model Lift Height
Model Lift Height is the distance the model is raised above the build plate before adding supports. We recommend using 5mm.
Orientation Quick Guide
Humanoids
- With a base: rotate the model back 20-45 degrees.
- Without a base: rotate the model back 5-15 degrees.
Creatures with four or more legs
- With a base: rotate the model back 45-55 degrees.
- Without a base: rotate the model back 25-45 degrees.

